News
New Assay For Early Detection of Aggressive Prostate Cancers Developed
by Camren Clouthier / Apr 13, 2021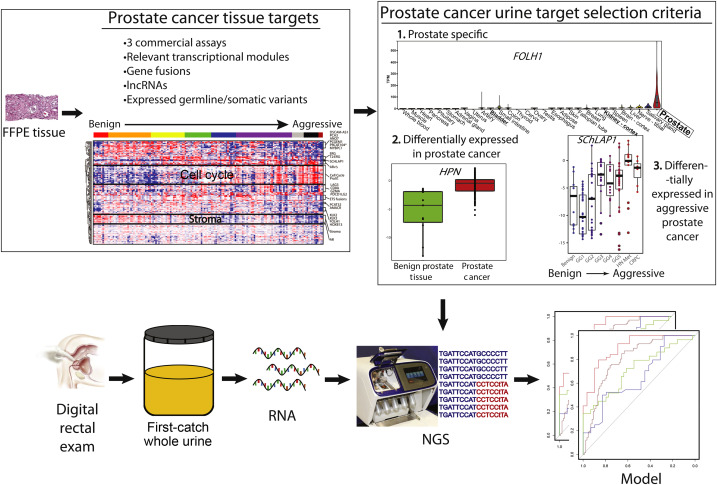 A new study, led by U-M graduate in molecular and celluar pathology Dr. Andi Cani, was just published in European Urology Oncology. The work includes contributions from several departmental faculty members including Drs. Aaron Udager, Arul Chinnaiyan, and Scott Tomlins, as well as a research team comprised of Chia-Jen Liu and Drs. Javed Siddiqui and Lanbo Xiao. The publication focuses on the development of a whole-urine, multiplexed, next-generation RNA-sequencing assay that is used for the early detection of aggressive forms of prostate cancer (PCa).
A new study, led by U-M graduate in molecular and celluar pathology Dr. Andi Cani, was just published in European Urology Oncology. The work includes contributions from several departmental faculty members including Drs. Aaron Udager, Arul Chinnaiyan, and Scott Tomlins, as well as a research team comprised of Chia-Jen Liu and Drs. Javed Siddiqui and Lanbo Xiao. The publication focuses on the development of a whole-urine, multiplexed, next-generation RNA-sequencing assay that is used for the early detection of aggressive forms of prostate cancer (PCa).
 "Our objective for the study was to improve on MiPS with a novel next-generation sequencing (NGS) multibiomarker urine assay for early detection of aggressive prostate cancer," Cani describes. The team started with the preclinical development and validation of a post-DRE urine RNA NGS assay assessing 84 PCa transcriptomic biomarkers, including T2:ERG, PCA3, additional PCa fusions/isoforms, mRNAs, lncRNAs, and expressed mutations. The UPSeq model was trained on 73 patients and validated on an omitted set of 36 patients, who represented the spectrum of disease.
"Our objective for the study was to improve on MiPS with a novel next-generation sequencing (NGS) multibiomarker urine assay for early detection of aggressive prostate cancer," Cani describes. The team started with the preclinical development and validation of a post-DRE urine RNA NGS assay assessing 84 PCa transcriptomic biomarkers, including T2:ERG, PCA3, additional PCa fusions/isoforms, mRNAs, lncRNAs, and expressed mutations. The UPSeq model was trained on 73 patients and validated on an omitted set of 36 patients, who represented the spectrum of disease.
This study supported the potential utility of the team's intitial novel urine-based RNA NGS assay to supplement PSA for improved early detection of aggressive PCa. "Our data support the continued development and prospective validation of this assay in larger patient cohorts for potential clinical applications in the evaluation of men at risk of PCa or aggressive PCa," Cani explains. "From a patient perspective, we have developed a new urine-based test for the detection of aggressive prostate cancer, which promises improvement upon current biomarker tests."
—
The full publication in European Urology Oncology is available here.