

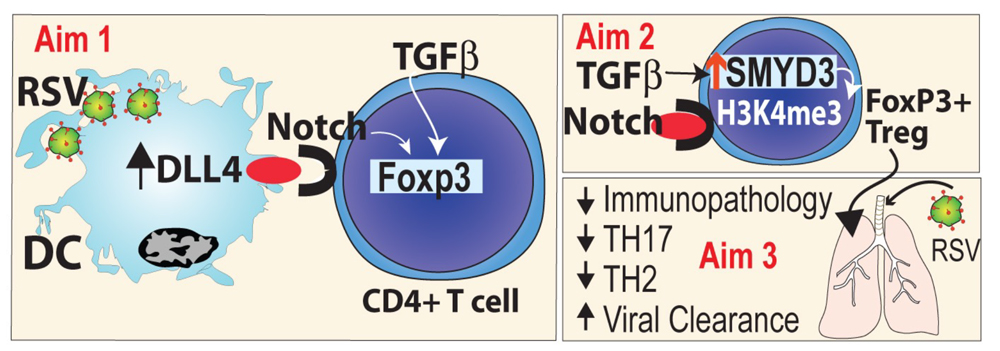
 Epigenetic regulation of gene activation is the organization of loci into transcriptionally active or silent states altering the accessibility of transcription factors and polymerases to gene promoters and enhancers. Chromatin wound around histones is regulated by the nature of the modifications to the protein tails of the histone core components, including H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. These modifications include methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, phosphorylation, etc, and determine the transcriptional status of the gene loci by exposing or sequestering the promoter region. Methylation of lysines on histone H3, especially H3K4 trimethylation, is associated with transcriptional activation and has been the most frequently studied modification. This activation mark on H3K4 is offset by methylation of H3K9 and H3K27, which are associated with transcriptional silencing of the gene. These modifications rely on both methyltransferases that add methyl groups and demethylases that remove methyl groups from specific lysines allowing plasticity to gene activation. Thus, the specific regulation of genes by chromatin modifications is likely both gene and cell specific; however, what these specific modifications are and how they work in the epigenetic control of DC and T cells is only beginning to be understood. Important, though, is the concept that histone modifications control access to gene promoters and enhancers for transcriptional regulation but do not directly activate genes. We have focused over the past several years on the alteration of both the T cell and DC that are epigenetically modified during RSV induced responses. Our publications have demonstrated that Smyd3, a H3K4 methyltransferase regulates Foxp3 expression through histone modification at the Foxp3 promoter and subsequently regulates RSV-induced immunopathology. We have further taken a rational approach to determine the role of Dll4/Notch in regulation of Smyd3 induced Treg cells. SMYD3 was previously identified as an H3K4me3-specific histone methyltransferase that may be a proto-oncogene based upon its expression in numerous cancers and due to the altered cellular function observed in overexpression studies of normal cells or in cellular silencing studies of SMYD3 in tumors. We were the first to identify the function and regulation of SMYD3 in immune cells. We have also shown that DC are epigenetically modified by the early life RSV infection. A key question has been whether the RSV infection and/or microbiome promote these innate immune cell changes.
Epigenetic regulation of gene activation is the organization of loci into transcriptionally active or silent states altering the accessibility of transcription factors and polymerases to gene promoters and enhancers. Chromatin wound around histones is regulated by the nature of the modifications to the protein tails of the histone core components, including H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. These modifications include methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, phosphorylation, etc, and determine the transcriptional status of the gene loci by exposing or sequestering the promoter region. Methylation of lysines on histone H3, especially H3K4 trimethylation, is associated with transcriptional activation and has been the most frequently studied modification. This activation mark on H3K4 is offset by methylation of H3K9 and H3K27, which are associated with transcriptional silencing of the gene. These modifications rely on both methyltransferases that add methyl groups and demethylases that remove methyl groups from specific lysines allowing plasticity to gene activation. Thus, the specific regulation of genes by chromatin modifications is likely both gene and cell specific; however, what these specific modifications are and how they work in the epigenetic control of DC and T cells is only beginning to be understood. Important, though, is the concept that histone modifications control access to gene promoters and enhancers for transcriptional regulation but do not directly activate genes. We have focused over the past several years on the alteration of both the T cell and DC that are epigenetically modified during RSV induced responses. Our publications have demonstrated that Smyd3, a H3K4 methyltransferase regulates Foxp3 expression through histone modification at the Foxp3 promoter and subsequently regulates RSV-induced immunopathology. We have further taken a rational approach to determine the role of Dll4/Notch in regulation of Smyd3 induced Treg cells. SMYD3 was previously identified as an H3K4me3-specific histone methyltransferase that may be a proto-oncogene based upon its expression in numerous cancers and due to the altered cellular function observed in overexpression studies of normal cells or in cellular silencing studies of SMYD3 in tumors. We were the first to identify the function and regulation of SMYD3 in immune cells. We have also shown that DC are epigenetically modified by the early life RSV infection. A key question has been whether the RSV infection and/or microbiome promote these innate immune cell changes.
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Breast team reviewing a patient's slide. (From left to right) Ghassan Allo, Fellow; Laura Walters, Clinical Lecturer; Celina Kleer, Professor. See Article 2014Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Autopsy Technician draws blood while working in the Wayne County morgue. See Article 2016Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Dr. Sriram Venneti, MD, PhD and Postdoctoral Fellow, Chan Chung, PhD investigate pediatric brain cancer. See Article 2017Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Director of the Neuropathology Fellowship, Dr. Sandra Camelo-Piragua serves on the Patient and Family Advisory Council. 2018Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Residents Ashley Bradt (left) and William Perry work at a multi-headed scope in our new facility. 2019Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Dr. Kristine Konopka (right) instructing residents while using a multi-headed microscope. 2020Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Patient specimens poised for COVID-19 PCR testing. 2021Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Dr. Pantanowitz demonstrates using machine learning in analyzing slides. 2022Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
(Left to Right) Drs. Angela Wu, Laura Lamps, and Maria Westerhoff. 2023Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Illustration representing the various machines and processing used within our labs. 2024Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
Rendering of the D. Dan and Betty Khn Health Care Pavilion. Credit: HOK 2025Department Chair |

newsletter
INSIDE PATHOLOGYAbout Our NewsletterInside Pathology is an newsletter published by the Chairman's Office to bring news and updates from inside the department's research and to become familiar with those leading it. It is our hope that those who read it will enjoy hearing about those new and familiar, and perhaps help in furthering our research. CONTENTS
|

MLabs, established in 1985, functions as a portal to provide pathologists, hospitals. and other reference laboratories access to the faculty, staff and laboratories of the University of Michigan Health System’s Department of Pathology. MLabs is a recognized leader for advanced molecular diagnostic testing, helpful consultants and exceptional customer service.